In the modern food industry, consumer expectations for consistency, hygiene, and convenience are higher than ever. From tomato paste and hot sauces to honey, salad dressings, jams, condiments, and ready-to-eat meal sauces, manufacturers must produce high-quality products quickly, safely, and efficiently. As demand continues to grow across retail, foodservice, and private-label markets, fully automated filling systems have become essential assets for food and sauce manufacturers worldwide.
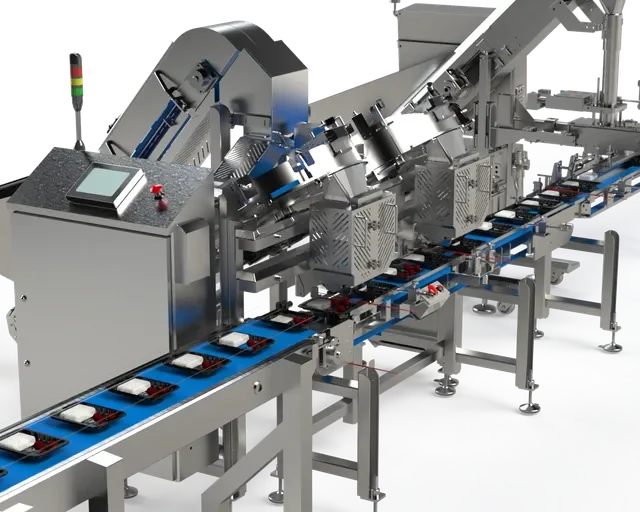
These systems replace manual or semi-manual operations with high-speed machinery, robotic movement, and intelligent controls—delivering faster throughput, better precision, and superior hygiene. This article explores the complete landscape of fully automated filling systems for food and sauce manufacturers, including how they work, what components they require, how to select the right system, and what benefits they bring. At the end, you’ll also see a recommended supplier—Micet—known for stainless-steel processing and filling equipment.
The Role of Fully Automated Filling Systems in the Food & Sauce Industry
Food and sauce products often require careful handling because they vary greatly in viscosity, temperature, texture, and particle size. Unlike beverages, which are often thin and flow easily, sauces may contain:
- High viscosity (ketchup, mayo, cheese sauce)
- Particles and inclusions (salsa, pesto, chili sauce)
- Sticky or sugary components (honey, fruit jam, caramel)
- Oil-water emulsions (salad dressing, tahini blends)
- Heat sensitivity (pasteurized or hot-fill products)
Automated filling systems are designed to handle these specific challenges while maintaining:
- Accurate volume control
- Stable product flow
- Minimal product waste
- Hygienic, contamination-free processing
- Efficient cleaning and sanitation
For sauce manufacturers, automation isn’t just a convenience—it’s a competitive advantage.
How Fully Automated Filling Systems Work
Fully automated filling lines integrate several synchronized modules to manage the entire packaging workflow:
- Container feeding and orientation
- Cleaning or sterilization (if required)
- Product dosing and filling
- Capping or sealing
- Labeling and coding
- Inspection and quality checks
- Packaging and palletizing
All operations are controlled through a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) and HMI (Human Machine Interface), which monitor speed, volume, pressure, temperature, and safety conditions.
The goal is to minimize human intervention for maximum hygiene and consistency.
Types of Filling Technologies Used for Food and Sauce Products
Different sauces require different filling mechanisms. Here are the most common technologies:
1. Piston Filling Systems
Best suited for:
- Thick sauces
- Tomato paste
- Fruit purees
- Nut butters
- Jam with fruit chunks
- High-viscosity condiments
Piston fillers provide extremely accurate volumetric filling and can handle sauces with particles up to a certain size.
2. Pump Filling Systems
Using lobe pumps or gear pumps, these systems handle:
- Medium-viscosity liquids
- Oil-based sauces
- Smooth dressings
- Syrups
They allow continuous filling at high speeds.
3. Gravity Filling Systems
Ideal for:
- Low-viscosity sauces
- Vinegar and liquid marinades
- Thin dressings
- Broth-based sauces
Gravity fillers maintain stable flow without damaging delicate ingredients.
4. Hot-Fill Systems
Used when the product must be filled at high temperature to ensure:
- Shelf stability
- Pasteurization
- Better bottle sealing
Perfect for ketchup, BBQ sauce, mustard, and many Asian sauces (soy-based, chili garlic, etc.).
5. Aseptic Filling Systems
Essential for shelf-stable sauces such as:
- UHT tomato sauces
- Retort pouch sauces
- Boxed soup bases
Aseptic filling lines offer extremely low contamination risk.
Key Components of a Fully Automated Sauce Filling Line
Product Holding and Preparation Tanks
Equipped with:
- Heating jackets
- Agitators
- Temperature control sensors
- Hygienic valves
These tanks keep sauces at the correct viscosity and temperature for filling.
Filling Machine
The heart of the system. Features may include:
- Multi-head fillers (4, 6, 8, 12+ heads)
- Servo-driven controls for high accuracy
- Adjustable filling volumes
- No-drip nozzles
- CIP-friendly design
Container Cleaning or Sterilization
For sterile products or food safety compliance:
- Air rinsers
- Water rinsers
- UV sterilization tunnels
- Steam sterilizers
Capping and Sealing Machines
Options include:
- Screw caps
- Snap caps
- Foil sealing
- Induction sealing
- Press-fit lids
Automation ensures consistent torque and seal integrity.
Labeling and Coding
Includes:
- Wrap-around labels
- Front/back labels
- Batch and expiry date printing
- QR code or traceability coding
Inspection Stations
Automated sensors check for:
- Correct fill levels
- Cap placement
- Label alignment
- Weight accuracy
- Foreign particles
Robotic Packaging Systems
Automates end-of-line functions:
- Tray loading
- Cartoning
- Shrink-wrapping
- Palletizing
Fully automated filling lines eliminate manual packing labor and reduce ergonomic risks.
Advantages of Fully Automated Filling Systems for Food & Sauce Producers
1. Higher Efficiency and Throughput
Production output increases dramatically:
- From hundreds per hour → thousands per hour
- Rapid changeovers for multiple SKUs
- Continuous operations with minimal downtime
This is crucial for competing in retail and wholesale markets.
2. Improved Product Consistency
Automation ensures:
- Stable portion sizes
- Better packaging uniformity
- Balanced ingredient distribution
- Precise temperature control
Consistency builds consumer trust and reduces returns or complaints.
3. Superior Hygiene and Food Safety
Automated lines:
- Reduce human contact
- Provide controlled environments
- Integrate tightly sealed filling zones
- Offer automated cleaning (CIP)
- Meet HACCP, GMP, and FDA standards
This minimizes contamination risks and supports regulatory compliance.
4. Lower Operational Costs
Although initial investment is higher, long-term savings include:
- Reduced labor dependency
- Less product loss due to overfilling
- Fewer errors and rejects
- Lower cleaning and sanitation costs
ROI for automated filling lines is often reached within 1–3 years.
5. Flexibility for Multiple Products
Modern automated lines can fill:
- Bottles
- Jars
- Jugs
- Pouches
- Cups
- Tubs
This supports product diversification and seasonal variations.
6. Scalability for Future Growth
As demand increases, manufacturers can:
- Add more filling heads
- Expand conveyor length
- Integrate advanced robotic packaging
- Increase tank capacity
Automation provides a scalable path for long-term expansion.
Setup Considerations for Sauce Manufacturers Investing in Automation
1. Sauce Viscosity and Flow Characteristics
Choose filling technology based on:
- Viscosity
- Presence of solids or chunks
- Temperature sensitivity
The wrong filler can cause clogging, inconsistent fills, or product damage.
2. Container Format
Determine the main formats you require:
- Glass jars
- PET bottles
- Squeeze bottles
- Pouches
Each format requires its own set of change parts.
3. Level of Hygiene Required
Products with low pH (like tomato sauces) may not require aseptic environments, while dairy-based sauces often do.
4. Temperature Requirements
Hot-fill lines require:
- Heat-resistant components
- Special seals
- Thermal-safe container handling
Cold-fill products demand careful microbial control.
5. Production Volume
Small startup? Mid-size processor? Industrial-scale?
Your automation level should match your growth stage.
6. Available Factory Space
A compact modular system works best for small facilities, while large plants can opt for fully extended monoblocks.
7. Utility Infrastructure
Automated filling lines require:
- Reliable electricity
- Compressed air
- Chilled water
- Steam or hot water
- CIP chemical supply
Upgrading utilities may be necessary.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Choosing an Automated Filling Line
- Ignoring product viscosity variations (hot vs cold filling changes flow significantly)
- Choosing a filler that cannot handle future SKUs
- Underestimating the need for CIP capability
- Buying only on price and ignoring build quality
- Not planning for realistic production growth
- Overlooking downtime and maintenance accessibility
Good planning avoids costly retrofits later.
FAQs
1. What is the best type of filling machine for sauces with chunks?
Piston fillers or rotary piston systems handle products with solids more effectively than pump or gravity fillers. They maintain portion accuracy while preventing clogging and shear damage to ingredients.
2. Can one automated filling line handle both hot-fill and cold-fill products?
Yes, but it requires special design considerations, such as heat-resistant seals, temperature-controlled tanks, and adaptable CIP cycles. Many manufacturers choose separate lines, but modern modular systems can handle both with the right configuration.
3. Are fully automated filling systems suitable for small food startups?
Absolutely. Compact automated lines with 2–4 filling heads are ideal for small producers who want professional packaging without high labor costs. These systems are designed to scale as production increases.
Why Micet Is Recommended for Fully Automated Food & Sauce Filling Systems
For food and sauce manufacturers seeking high-efficiency, hygienic, and long-lasting filling equipment, Micet is a trusted supplier known for stainless-steel engineering and turnkey production-line solutions.
Micet provides:
- Fully automated piston, pump, gravity, and hot-fill systems
- Custom solutions for ketchup, chili sauce, honey, jam, dressings, dips, and more
- High-grade 304/316 stainless-steel tanks, mixers, and CIP systems
- PLC/HMI control systems for accurate and stable filling
- Modular filling lines that support bottles, jars, pouches, and specialty containers
- Comprehensive engineering design, including 2D/3D layout planning
- Installation guidance, operator training, and ongoing technical support
- Strong export-quality fabrication with competitive pricing
